Overview
Building things in the cloud can feel overwhelming. So many choices…
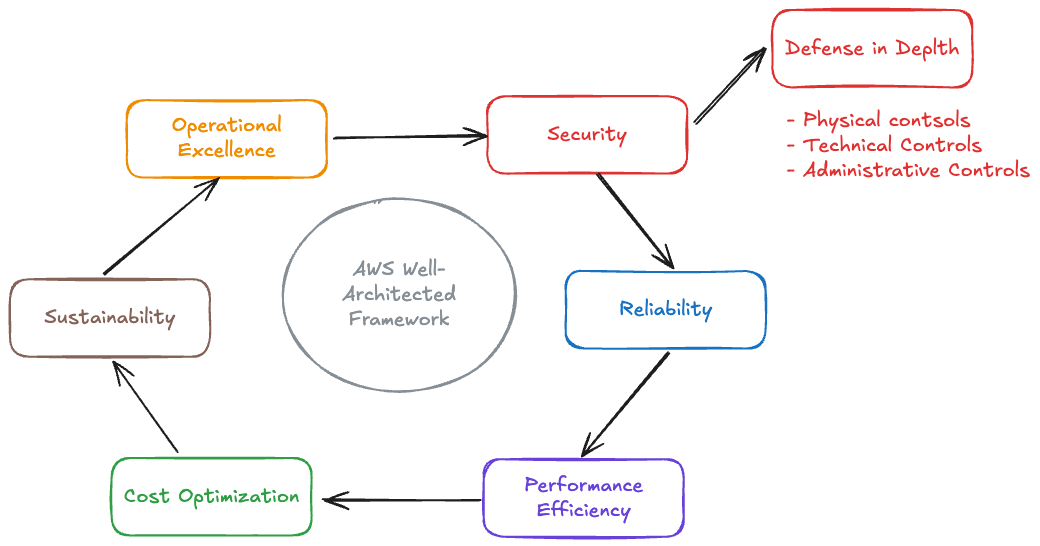
That’s where the AWS Well-Architected Framework comes in. It’s basically AWS handing you a checklist so you don’t forget the important details when designing or reviewing your systems. Let’s walk through them one by one:

The Six Pillars
The framework consists of six pillars that work together to help you build secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient infrastructure:
Operational Excellence
What it means: Running your systems smoothly every day and learning from mistakes, automating everything possible, and improving continuously
AWS Services:
- AWS CloudFormation and AWS CDK for infrastructure as code
- Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring and observability
- AWS Systems Manager for operational insights and automation
- AWS X-Ray for distributed tracing and debugging
Exam tip: Manual processes = bad. Questions often test “How to automate deployments?” (Answer: CodePipeline + IaC)
Security
What it means: Keeping your data and systems safe from threats with defense in depth (multiple layers).
Defense in Depth - Three Control Types:
- Physical Controls: Data center security, hardware security modules, physical access controls
- Technical Controls: Encryption, authentication, firewalls, intrusion detection
- Administrative Controls: Policies, procedures, training, access reviews
AWS Services:
- AWS IAM for identity and access management
- AWS KMS for encryption key management
- Amazon GuardDuty for threat detection
- AWS Security Hub for centralized security management
- AWS WAF for web application firewall protection
Exam trap: Overly broad permissions. Security is foundational - it impacts every other pillar.
Reliability
What it means: Making sure your system works when people need it. In the cloud, failures will happen, and we should design systems that are resilient by default. Systems recover quickly from failures and meet demand
Critical Concepts:
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): Maximum acceptable downtime
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): Maximum acceptable data loss
- Multi-AZ Deployment: Distribute resources across availability zones
- Backup Strategy: Regular automated backups with tested restore procedures
AWS Services:
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling for automatic capacity adjustment
- Elastic Load Balancing for traffic distribution
- Amazon RDS Multi-AZ for database availability
- Amazon Route 53 for DNS and health checks
- AWS Backup for centralized backup management
Exam tip: Single AZ deployment. Classic question: “Outage in one AZ - how to stay up?” (Multi-AZ + Route 53 failover).
Performance Efficiency
Focus: Using the right amount of computer power for what you need. It is about choosing the right resources for the job and continuously optimizing as the workload evolves.
AWS Services:
- Amazon CloudFront for content delivery and caching
- AWS Lambda for serverless compute
- Amazon ElastiCache for in-memory caching
- Amazon RDS with read replicas for database performance
- AWS Compute Optimizer for resource recommendations
Exam tip: Over-provisioning for peak load. Use Auto Scaling to match demand.
Cost Optimization
What it means: Getting the most value for your money. It is not about choosing the cheapest options - but achieving your business outcomes efficiently and avoiding unnecessary expenses.
Ways to save money:
- Right-sizing: Pick the correct server size
- Reserved Instances: Pay upfront for big discounts
- Spot Instances: Use spare capacity for cheap
- Storage tiers: Move old data to cheaper storage
AWS Services:
- AWS Cost Explorer for cost analysis and forecasting
- AWS Budgets for cost monitoring and alerts
- AWS Compute Optimizer for right-sizing recommendations
- AWS Trusted Advisor for cost optimization checks
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering for automatic storage optimization
Exam tip: “Cheapest” ≠ optimal. Balance with performance/reliability.
Sustainability
What it means: Using less energy and reducing waste. Sustainability might feel like a ’nice-to-have’ now, but it’s becoming table stakes fast. This is the newest pillar. It’s about being better for the environment while running your systems.
AWS Services:
- AWS Graviton processors for energy-efficient compute
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering for storage optimization
- AWS Fargate for optimized container operations
- AWS Lambda for serverless efficiency
- AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool for tracking emissions
Exam note: Often paired with Cost Optimization (efficiency saves money + CO₂).
How the Pillars Work Together
- Security impacts everything: Security controls must be implemented across all pillars without compromising performance, reliability, or cost
- Performance and Cost: Over-provisioning hurts cost optimization, under-provisioning hurts performance - find the right balance
- Reliability and Operational Excellence: Good operational practices lead to reliable systems, and reliable systems are easier to operate
- Sustainability and Cost: Efficient resource use benefits both the environment and your budget
- Performance and Sustainability: Optimized code and efficient architectures reduce both latency and carbon footprint
Summary
The AWS Well-Architected Framework provides a consistent approach for evaluating cloud architectures. Remember these key points:
- Start incrementally - You don’t need perfect architecture on day one
- Use the pillars as a checklist - Review each pillar during design and regular reviews
- Balance tradeoffs - Optimizing one pillar often affects others
- Iterate and improve - Architecture evolves with your workload
Next Steps:
- AWS Solutions Architect Certification - Official certification page
- AWS Well-Architected Tool - Free tool to review your workloads
Looking for more AWS content? Check the aws tag for related posts.